Faculty Mentor
Dr. Elaine Vanterpool
Files
Download Full Text (518 KB)
Description
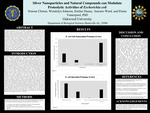
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic bacterium that naturally resides in the human gastrointestinal tract as a commensal microorganism. While non-pathogenic strains contribute to digestion and vitamin production, certain pathogenic strains can cause a wide range of diseases, from mild gastrointestinal discomfort to severe illness. A key factor in its pathogenicity is the production of protease enzymes that break down proteins which play a crucial role in bacterial survival and virulence. This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of different antibacterial compounds in inhibiting the function of both secreted and cell-associated E. coli protease activity.
Publication Date
2025
City
Huntsville
Disciplines
Biology
Recommended Citation
Vanterpool, Elaine, "Silver Nanoparticles and Natural Compounds can Modulate Proteolytic Activities of Escherichia coli" (2025). Student Posters. 75.
https://ouscholars.oakwood.edu/student-posters/75