-

Effects of Cell-Free Supernatants of Commercial Yogurt Products on Salmonella Survival
Juliet Durant and Akayla King
Salmonellosis remains a global public health challenge and Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis and Typhimurium are the primary causes. Salmonella virulence mechanisms involve attachment and invasion of intestinal epithelial cells. Gut microbiota and probiotics that contain Lactobacillus species have been shown to prevent Salmonella infection. Yogurt is a commonly consumed probiotic product containing Lactobacillus species. Yogurts made under laboratory conditions and the cell-free supernatants have been shown to inhibit Salmonella growth. The many commercial yogurt products on the market may vary in antimicrobial components based on production methods. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the survival of 5 log CFU/mL of Salmonella inoculated into cell-free supernatants (CFS) of the following types of commercial yogurts: Greek whole milk plain, Greek nonfat plain, Greek nonfat vanilla, Greek zero sugar vanilla and dairy free almond milkfat. Trypticase soy broth adjusted to pH 4.5 served as the control. The CFS for all yogurt products inhibited the growth of S. typhimurium as zero CFU were observed on Tryptic Soy agar after 24 and 48 h incubation at 37°C, compared to 7.6±0.8 log CFU/mL at 24 h and with the control. Our findings suggest that commercial yogurts produce bioactive compounds that inhibit S. typhimurium growth. Because the human gut environment is complex, in vivo studies are needed to determine the impact of commercial yogurts on salmonellosis.
-

Analyzing the Inhibition Of Chemical Compounds On Protease in P. aeruginosa
Elaine Vanterpool
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a gram-negative, bacillus-shaped opportunistic pathogen, notorious for invading immunocompromised individual leading to secondary infections. These opportunistic microbes typically are implicated mild to more severe infections including burn or wound infections to more serious systemic infections. The bacterium Ps. aeruginosa utilizes a variety of virulence factors to enhance the pathogenicity of the organism. Virulence factors secreted by Ps. aeruginosa include its pili, adhesins, capsule, exotoxin A, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The proteases produced by Ps. aeruginosa are powerful virulence factors that can lead to tissue destruction and immune invasion. It is imperative that we find ways of regulating the proteases of this organism.
-

Improving Biocompatibility and Structural Integrity of Decellularized Biomaterials
Elaine Vanterpool
Tissue engineering is a revolutionary approach to regenerative medicine. Within the field of tissue engineering, biomaterials such as the great saphenous vein or synthetic materials such as PET, are used in tissue generation for grafts and wound healing in many other uses. This is promising and has the potential to save many lives, but many glaring issues prevent the use of these scaffolds in a clinical setting. Some of these include body rejection, lack of hemocompatibility, and weak structural integrity.
-
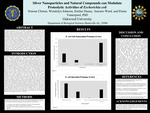
Silver Nanoparticles and Natural Compounds can Modulate Proteolytic Activities of Escherichia coli
Elaine Vanterpool
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic bacterium that naturally resides in the human gastrointestinal tract as a commensal microorganism. While non-pathogenic strains contribute to digestion and vitamin production, certain pathogenic strains can cause a wide range of diseases, from mild gastrointestinal discomfort to severe illness. A key factor in its pathogenicity is the production of protease enzymes that break down proteins which play a crucial role in bacterial survival and virulence. This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of different antibacterial compounds in inhibiting the function of both secreted and cell-associated E. coli protease activity.
-

Silver Nanoparticles and Vanillin Can Inhibit Collagenase Activities of Serratia marcescens
Elaine Vanterpool
Serratia marcescens is a gram-negative, disease-causing agent that belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family. This rod-shaped microbe causes many infectious diseases such as urinary and respiratory infections, wound infections, and peritonitis, which can result in fatal bacteremia. Protease is a virulence factor of S. marcescens that enhances its pathogenicity by breaking down proteins via cleavage of peptide bonds. The purpose of this research is to identify testing agents that reduce the protease mediated pathogenicity of S. marcescens
-

Using Secreted Biomarkers in the Development of the Detection of Advanced Cancer Screening System
Elaine Vanterpool
An estimated 20 million people globally develop cancer every year. Furthermore, over 9.7 million people die from cancer. The best prognosis of cancer occurs when detected early. Cancer, in its early stages, usually does not display clinical symptoms and is usually not detectable by symptoms and is diagnosed later. The goal of the D.A.C.S. is to provide a screen that can detect cancer. It is hypothesized that developing a cancer detection system/technology, named D.A.C.S. (Detection of Advanced Cancer Screening) system, can help with early cancer detection, while still being affordable for the general public.
-

Analysis of Cys294Arg Mutation in CS1 Associated with Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome & Collagen Degradation
Elaine Vanterpool and Amy Aboki
C1s enzyme plays a crucial role in the immune system so that the body can fight infection and repair damaged tissues. However, if it is not working properly, it will do more harm than good. This is shown in the case of periodontal Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (pEDS), a rare genetic disorder whereby C1s breaks down collagen I, a protein that gives structure and strength to connective tissues. Severe gum disease, loose teeth and premature teeth is a result of this. The purpose of this study is to identify and analyze the pathogenicity of C1s mutations and association in pEDS.
-

Analysis of CD36 variants associated with Heart Disease
Elaine Vanterpool and Lemanisha Adams
Cardiovascular/Heart Disease (CVD) is commonly characterized when coronary arteries struggle to supply the heart with enough blood, oxygen, and nutrients. Some symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, pain in the neck, numbness, weakness, or coldness in the arms or legs, dizziness or fainting, and fatigue or exhaustion. Cardiovascular disease affects an estimated 47-54% of Black adults in America (Cleveland Clinic). The purpose of this study is to identify and assess the pathogenicity of the CD36 variants associated with cardiovascular disease.
-

Defective Sickle Cell Mutations
Elaine Vanterpool and Carroline Anderson
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. It is an inherited hemoglobinopathy. Both alleles must be affected to manifest the disease. In sickle cell disease, the red blood cells become hard, sticky, and look like a sickle, making it difficult to pass through the blood vessels and carry oxygen. Sickle cell trait is more prevalent than sickle cell disease and affects 1 in 13 African American babies (According to the CDC). The clinical manifestation of sickle cell trait is not as aggressive and does not cause as much morbidity as sickle cell disease. This study aimed to identify the gene variants associated with sickle cell disease.
-

An analysis of HTT involvement in Huntington’s Disease
Elaine Vanterpool and Micah Andrews
Huntington's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by loss of striatal neurons. These striatal neurons are essential in cognition, motor function, decision-making, motivation, reinforcement, and reward perception. Affected individuals may show symptoms such as isolation, lack of motivation, depression, mood swings, and personality changes. This study’s purpose is to analyze and highlight the variants of the HTT gene in the pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease.
-

HYDIN Gene Variants: Implications in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia and Other Diseases
Elaine Vanterpool and Sharie Angus
HYDIN is a gene that encodes a protein potentially involved in cilia motility. Mutations in this gene cause autosomal recessive primary ciliary dyskinesia-5, a disorder characterized by cerebrospinal fluid accumulation within the brain's ventricles. This study aims to identify and assess the pathogenicity of HYDIN variants.
-

Impact of MSX1 and IRF6 Gene Variants on Orofacial Cleft and Facial Development
Elaine Vanterpool and Lia Banks
A cleft lip or palate is a congenital anomaly that occurs when a baby's mouth doesn’t form properly during pregnancy. It happens when the tissues that shape the upper lip or roof of the mouth fail to join during development. It is among the most common birth defects associated with genetic conditions or syndromes. Orofacial cleft can be caused by a combination of genes and other factors like the mother's exposure to environmental things, diet, and medications during pregnancy. Examining the genes involved and making connections that provide insight into the improper formations of the maxillary tissues during fetal stages is crucial. This study used Simple Clinvar, Uniprot, Polyphen 2, SIFT, and SWISS Modeling to identify and analyze mutations.
-

An Analysis of DNAJC13 Variants Associated with Parkinson’s Disease
Elaine Vanterpool and Rhadames M. Batista-Mendez
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons, leading to motor impairments such as tremors, rigidity, and postural instability. Affecting millions worldwide, PD has been linked to both genetic and environmental factors. This study aims to identify and assess the pathogenicity of DNAJC13 variants associated with Parkinson's disease.
-

Analysis of KCNJ2 Variants Associated with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
Elaine Vanterpool and Kerenlaime Bautista
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is a cardiac disorder characterized by an accessory electrical pathway, leading to tachycardia and arrhythmias. It is diagnosed via electrocardiogram (ECG), showing a shortened PR interval and delta wave. WPW is typically managed with medications, catheter ablation, or surgery. Although primarily caused by anatomical anomalies, emerging research suggests genetic factors, including ion channel mutations, may contribute to the condition. The KCNJ2 gene encodes an inward-rectifier potassium channel critical for cardiac excitability. Mutations in KCNJ2 are linked to Andersen-Tawil syndrome, a disorder featuring arrhythmias and muscle weakness, raising questions about its role in WPW. This study investigates whether KCNJ2 variants influence WPW syndrome, potentially affecting its severity.
-

Mutations in the MMP20 Gene in Association with Amelogenesis Imperfecta
Elaine Vanterpool and Alicia Broomfield-Myrie
Enamel, the hardest substance in the body, protects the teeth from various forces like temperature and physical factors that would cause damage. Depending on the kind of AI one has developed, the phenotypes can range from thin teeth to teeth discoloration or decay. MMP20, a gene commonly associated with AI, encodes for Enamelysin, a protein crucial for enamel formation. It is also known as matrix metallopeptidase 20. It becomes active when it is cleaved by cellular proteases. When this gene is mutated, the splicing pattern is altered. Consequently, this can cause disease. This study was developed to analyze the pathogenicity of the mutated MMP20 variants associated with AI.
-

The Duality of the BARD1 Gene
Elaine Vanterpool and Khadra Burden
Breast cancer is the 2nd most diagnosed cancer in women in the United States (Mayo Clinic). Cancer is the overproduction of cells. In other words, cancer-infected cells continue to grow and may cause large growths called tumors. Although there have been innumerable strides in breast cancer research, the exact cause for breast cancer is not yet known (Mayo Clinic). It is believed that factors such as family history of the disease, early menstruation age, and obesity can increase an individual’s chances of having breast cancer. One of the well-known genes associated with breast cancer is BRCA1. A much less researched gene associated with breast cancer is BARD1 (BRCA1 associated ring domain 1). ClinVar identified the BARD1 gene to be connected to breast cancer, and over 1000 missense variants. Most of the variants had uncertain/conflicting clinical significance. ClinVar also identified the single nucleotide variants Pro7Ser and Cys71Tyr as missense mutations linked to BARD1. Pro7Ser had an uncertain/conflicting clinical significance and Cys71Tyr was classified as pathogenic. SIFT and PolyPhen2, bioinformatics software, determined that the Cys71Tyr mutation is probably damaging, and the Pro7Ser mutation is benign. The BARD1 gene’s FASTA sequence was placed into the SWISS-Model software to create a 3D protein model. These findings further support previous studies on the correlation between familial breast cancer and the BARD1 gene.
-

HBB Gene and Sickle Cell Disease
Elaine Vanterpool and Adia Burley
Sickle cell disease affects the shape of the red blood cells in our body, which can affect the oxygen carried to the rest of the body. The red blood cells become sickle-shaped, making it harder to pass through the body. Sickle cell disease affects around 100,000 people in the United States (CDC). More than 90% are African American or non-Hispanic black, and 3%-9% are Hispanic or Latino (CDC). Some mutations have been reported that are related to sickle cell disease, with HBB mutations highly correlated with sickle cell. This study aims to evaluate the specific missense mutations associated with HBB.
-

Analysis of DMD Variants Associated with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Elaine Vanterpool and K’sia Byass
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is an X-linked recessive disorder that causes muscle weakness. This disease is characterized by frequent falls, difficulty walking, running, jumping, or scoliosis. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy 1 in every 5000 boys worldwide causes a gene tic mutation that prevents the production of dystrophin. This study aims to identify and assess the pathogenicity of DMD variants associated with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Genetic mutations responsible for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy have been reported. Studies regarding DMD and its specific role in causing Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy have been reported to be accurate and effective. X-linked inheritance patterns are applied to this disease's pathogenesis and genetic and environmental factors. ClinVar was used to identify the DMD as a gene associated with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and the multiple variants, single nucleotide missense mutations, p.Lys765Glu, p.His446Arg, and p.Thr715Ser. The DMD gene codes for a dystrophin cytoskeletal protein, a scaffold protein that is a crucial link between sarcolemma and actin cytoskeleton that helps stabilize muscle fibers during contraction. Pathogenic mutations in DMD are known to alter the expression of specific muscle tissues. The DMD protein is expressed in most skeletal and heart muscles. Computational tools SIFT and PolPhen-2 were used to determine the pathogenicity of the three variants.SIFT predicted the p.Lys765Glu to be damaging, p.His446Arg to be tolerated, and p.Thr715Ser to be tolerated. On the other hand, Polphen-2 predicted p.Lys765Glu to be damaging, and the other two mutations were benign. The pathogenicity of these mutations suggests that the functionality of the dystrophin cytoskeletal protein was affected, which also potentially affects the gene expression and the X chromosome within the spine. Previous studies have connected pathogenic mutations in DMD to Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy as they have implicated in dilated cardiomyopathy, which is observed in those with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.
-

Bioinformatics Analysis of the MBL2 Missense Variants Associated with Cystic fibrosis
Elaine Vanterpool and Kiar-Ra Cameron
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an autosomal recessive disease commonly recognized by thick mucus and loud coughs. The manifestation of these symptoms is due to the inability of chloride ions to diffuse out of the cell. Thus, preventing osmosis resulting in a thick mucus on the lung’s surface. Those who suffer from this disease have difficulty breathing and require a modulator with a vest to increase gas exchange in the lungs. Moreover, the disease can result in much pain due to coughs, which destroys ciliated epithelial cells. Patients who have cystic fibrosis can suffer from pneumonia and other bronchial infections. They also experience difficulties with secretions out of exocrine glands. The low-frequency gene, Mannose Binding Lectin-2 (MBL2) associated with cystic fibrosis was analyzed for this study. This gene encodes for a protein that plays an integral role in the innate immune system. It binds to the mannose and N-acetylglucosamine found on the surface of pathogens. It then removes the pathogen by signaling the lectin complement system and phagocytic cells. The purpose of this study was to observe the missense mutations within this gene. Computational tools were used to view the mutated variants, the 3-D modelling, and conserved domains. The simple ClinVar database identified variants within this gene. Polyhen2 was used to analyze the pathogenicity of Gly54Asp and Pro101Leu. The computational tool predicted Gly54Asp as "probably damaging” with a 1.00 sensitivity score. The Pro101Leu swap was deemed to be “benign” with a sensitivity score of 0.043. Upon further analysis, the SIFT tool predicted the substitution to affect the protein. The second variant, Pro101Leu was predicted to be "tolerated". The SWISS modelling further identified the physical changes in the protein structure. Analysis of mutations within this gene can prevent other infections; ultimately, preventing the exhibition of cystic fibrosis.
-

An Analysis of CAPN-10 Variants Associated with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Elaine Vanterpool and Azaria Carey
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrinopathy in 6-13% of females. Small fluid filled sacs develop along the outer edge of the ovarian lining, later turning into cysts. These contain immature eggs, called follicles, which regularly fail to release. The exact cause of PCOS is unknown. Although, along with early diagnosis, treatment, and weight loss, these routine factors may lower the risk of long-term complications such as type-2-diabetes and cardiovascular diseases (Mayo Clinic). This study’s purpose is to identify and access the pathogenicity of CAPN-10 variants associated with PCOS.
-

Analyzing the Inhibition Of Chemical Compounds On Collagenase in P. aeruginosa
Elaine Vanterpool, Marielle Cooper, and KiaRa Cameron
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic pathogen that poses significant challenges in clinical treatment due to its production of collagenase. This bacterium can cause several infections including pneumonia, meningitis, septicemia, and a host of other diseases. Collagenase acts as a key virulence factor by breaking down collagen in the host’s extracellular matrix, allowing bacteria to invade tissues. This study hypothesized that the effects of cell secreted collagenase would be inhibited by metronidazole, vanillin, and silver nanoparticles to reduce the pathogenicity of Ps. aeruginosa related infections.
-

An analysis of VHL and its relation to Leukemia
Elaine Vanterpool and Marquise De Velde
Leukemia is a special type of cancer caused by the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells. It is the cancer of blood-forming tissues such as the bone marrow, making it difficult to fight against foreign agents. Leukemia is the 10th most common cancer accounting for 3.1% of all new cancer cases and 3.9% of all cancer deaths (National Institute of Health). The purpose of this study is to analyze the potential genetic mutations or variants associated with the leukemia phenotype.
-

An Analysis of ABCA3 variants Associated With Hypertension
Elaine Vanterpool and Lisa-Faith Dieujuste
Hypertension is a condition that affects the arteries of a person. It occurs when the blood pressure in the body is too high. A medical condition that is well known to be one of the major causes of premature deaths worldwide. Affecting an estimation of 1.28 billion adults (World Health Organization). This study’s purpose is to identify and assess the pathogenicity of ABC3 variants associated with Hypertension.
-

An Analysis of DAGLA Variants Associated with ADHD
Elaine Vanterpool and Zahra Dulan
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impulsivity, difficulty focusing and staying on task, hyperactivity, including restlessness and excessive talking, and deficits in working memory. Individuals with ADHD may also struggle to maintain relationships, regulate emotions, and stay organized. The DAGLA gene has been associated with the ADHD phenotype and is primarily located in brain tissues. It is responsible for encoding diacylglycerol lipase alpha, an enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of key endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG). This protein has been shown to play a major role in central nervous system development and synaptic elasticity. This study serves to identify variants of the DAGLA gene associated with ADHD and determine their pathogenicity.
-
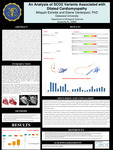
An Analysis of SCO2 Variants Associated with Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Elaine Vanterpool and Mitspah Eshette
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. DCM affects an estimated 25-35% of individuals have familial forms of the disease, with most mutations affecting genes encoding cytoskeletal proteins, while some affect other proteins involved in contraction. The disease is genetically heterogeneous, but the most common form of its transmission is autosomal. This study's purpose is to identify and assess the pathogenicity of the synthesis of cytochrome C Oxidase (SCO2) variants associated with DCM.
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.